Initial Memo: Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TPE:2330), 67% 5-Year Potential Upside (Calista CHEW, EIP)
Calista suggests a "Hold" for TSMC, with prices slightly inflated after riding on the exponential revenue growth experienced by Nvidia and could potentially take a hit in 2024.
LinkedIn | Calista CHEW
Company Overview
Established in 1987 and headquartered in Hsinchu Science Park, Taiwan, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) was the pioneer of the pure-play foundry business model. Led by Morris Chang who revolutionized the semiconductor industry, TSMC's adoption of the foundry business model has been instrumental in shaping the global fabless industry, solidifying its position as a leading semiconductor foundry by providing American chip companies with cost-effective manufacturing solutions. This model is distinguished by its exclusive focus on manufacturing its customers' products, abstaining from designing, manufacturing, or marketing any semiconductor products under its own name. This deliberate choice ensures that TSMC never enters into competition with its customers. As of 2023, the company has produced 11,895 different products using 288 distinct technologies for 528 different customers.
TSMC's semiconductors cater to a vast and varied global customer base, serving diverse applications across numerous end markets. These products find utility in high performance computing, smartphones, the Internet of Things (IoT), automotive technology, and digital consumer electronics. This broad diversification serves to mitigate fluctuations in demand, allowing TSMC to sustain high levels of capacity utilization and profitability while ensuring robust returns for future investments.
Business Segments
Foundry Services: TSMC is primarily known for its foundry services, where it manufactures semiconductor products based on designs provided by its customers. This is the core business segment of TSMC and includes the manufacturing of a diverse array of ICs using various process technologies.
Technology Development and Research: TSMC invests heavily in research and development (R&D) to advance semiconductor manufacturing technologies. This involves developing and refining new process nodes, materials, and manufacturing techniques to enhance the performance, power efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of ICs.
Design Enablement: TSMC provides design enablement services to its customers, including design tools, libraries, and intellectual property (IP) blocks. These resources help customers optimize their IC designs for TSMC's manufacturing processes, ensuring efficient production and high-performance end products.
Customer Support and Services: TSMC offers comprehensive customer support and services to assist customers throughout the design, manufacturing, and testing phases. This includes technical support, engineering consultation, and collaboration on product development projects.
Cost Drivers
The historical trend of decreasing average selling prices (ASP) for end-use applications exerts downward pressure on the prices of the components used in these applications. Lower ASPs for end-use products may lead to increased pricing pressure on components produced by TSMC, potentially affecting the company's revenue, margins, and earnings negatively. This trend aligns with Moore's Law, which predicts that the number of components on a single chip doubles approximately every two years at minimal cost. However, it is anticipated that the physical limits of Moore's Law may be reached in the 2020s. Chip-makers face challenges such as rising costs to continue meeting the industry standards set by Moore's Law and the difficulty of cooling an increasing number of components in a confined space. For example, as components are miniaturized, more can fit into a one-inch square chip, but this also results in higher heat generation, making cooling more challenging. Therefore, the physical limits of Moore’s Law could exert an upward pressure on ASP.
The initial costs of operating fabrication sites in US and the cost of ownership for advanced logic chips are higher than in its home market due to a number of factors. Firstly, TSMC faced challenges finding skilled workers, such that it trained many of the 1,100 local staff at its facilities in Taiwan. Next, US has imposed additional restrictions on the sale of AI chips to China to promote the US semiconductor growth and to protect national security.
Management
CEO
Dr. C. C. Wei is the Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of TSMC as of June 2024. He has held various positions within TSMC, including:
Chief Executive Officer (June 2018 - June 2024)
President and Co-CEO (November 2013 - June 2018)
Co-Chief Operating Officer (March 2012 - November 2013)
Senior Vice President of Business Development (2009 - 2012)
Senior Vice President of Mainstream Technology Business
Before joining TSMC in 1998, Dr. Wei worked at:
Chartered Semiconductor as Senior Vice President of Technology
ST Microelectronics as Senior Manager, Logic and SRAM technology development
Texas Instruments R&D organization as a Member of Technical Staff
He holds a B.S. degree in electrical engineering from National Chiao Tung University and a Ph.D. from Yale University.
Other Key Executives
Industry Analysis
Currently, TSMC is operating on a global scale with a focus on North America market.
Figure 1 shows the breakdown of the countries that TSMC is operating in.
Business Models
Integrated circuits (ICs), commonly known as chips, are diminutive electronic components often hailed as the cognitive centerpieces of electronic products. As the semiconductor industry has advanced, it has given rise to various business models, with three primary ones emerging: integrated device manufacturers (IDMs), design houses, and foundries. Design houses specialize in IC design, while foundries handle IC manufacturing for external companies, leading to the establishment of collaborative alliances between fabless companies and foundries. These alliances serve to mitigate investment risks and optimize operational efficiency. Consequently, many IDMs, such as Intel, Samsung, and Micron, have transformed themselves into IDM-Foundry hybrids to engage in both IC design and IC manufacturing to maintain competitiveness.
This dynamic engenders a cooperative rapport between design houses and foundries, while a blend of competition and collaboration describes the relationship between IDMs and foundries. The collaboration between IDMs and foundries occurs as IDMs may opt to outsource manufacturing tasks to foundries during periods of constrained capacity. For instance, Intel leverages TSMC's 6mm FinFET process for its manufacturing needs.
Market Size
Semiconductors are essential electronic circuits or units that serve as vital components in nearly every modern electronic device, ranging from transistor radios to iPhones. These components are vital to electronic devices and systems, encompassing memory devices, logic devices, analog integrated circuits, memory protection units, microcontroller units, discrete power devices, among others. With the semiconductor manufacturing industry currently valued at $681.05 billion, the industry growth is projected to be exponential, reaching $2062.59 billion by 2032 with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.9% from 2024 to 2032.
The global semiconductor industry is poised for growth due to the expanding use and integration of electronics across various applications such as networking communication devices, data processing, industrial automation systems, consumer electronics, automotive technologies, and government projects. In addition, the growth of consumer electronics worldwide further fuels market expansion.
Furthermore, semiconductors play a pivotal role in the advancement of AI technology, requiring improved memory chip processing capabilities for swift data handling. The escalating demand for faster and more advanced memory chips in data centre applications is anticipated to drive market growth. According to Bloomberg Intelligence, the generative AI market is expected to expand rapidly, reaching $1.3 trillion over the next decade from $40 billion in 2022. Given that semiconductor manufacturers provide the essential components for AI technology, the semiconductor industry is poised to undergo similar growth and consequently, expand the market size of semiconductors.
Competitor Analysis
TSMC crafted and maintained its market position by focusing its business model solely on the production of semiconductors. However, the semiconductor industry is very segmented with fabless companies designing the chipsets and foundries manufacturing the final product. While some companies choose to become IDMs to design and manufacture their own chips, TSMC decided not to manufacture any products under its own name, so that the company never engages in direct competition with its customers.
The competition in the semiconductor foundry industry is fierce as TSMC competes with other foundry service providers and some Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs). However, as chip designs grew increasingly complex, requiring specialized manufacturing skills, TSMC and Samsung emerged as the only companies with the necessary expertise. Samsung, despite its capabilities, faced challenges. Firstly, its dual role as a chip designer led many advanced designers to doubt its impartiality due to the competitive nature of relationship between design houses and IDM-based foundries. Next, its lower yield rates and poor chip performance meant customers often paid for non-functional chips, driving its customers towards its competitors. For example, while Samsung may be the first to transition to GAAFET for its 3nm chips, it faces challenges in scaling up its capabilities due to poor yield and low adoption rates. Consequently, seven tech giants, including Nvidia, AMD, Intel, Qualcomm, MediaTek, Apple and Google, have decided to use TSMC’s 3nm process. Therefore, TSMC became the preferred choice for manufacturing the most advanced chips.
Figure 2 shows that TSMC is the second largest semiconductor company worldwide and has a 13% market share.
Focusing solely on chips manufacturing, TSMC is the world’s largest producer of semiconductors and the main supplier for large-tech companies. TSMC dominates the market with 53% share in chip manufacturing and over 91% share in advanced chip manufacturing, serving as the exclusive manufacturer for tech giants like Apple and Nvidia. Despite IDMs having their own foundry capabilities, Intel relies on TSMC for its cutting-edge chip production, highlighting the intricate dynamics of the chip manufacturing industry, where expertise, trust, and reliability play critical roles in shaping market dominance and technological advancement.
Economic Moat
High Capital Intensity and Cost Barrier
TSMC operates in an industry that requires immense capital investment. For instance, equipment like the Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography (EUV) machine is essential for advanced semiconductor manufacturing but costs around $150 million per unit. This creates a significant barrier to entry for competitors who must also invest heavily to compete at TSMC's level. Moreover, securing these machines is difficult due to high demand and limited supply, further solidifying TSMC's advantage.
Complexity in Operations
Operating advanced semiconductor manufacturing equipment like the EUV machine requires specialized knowledge, extensive training, and ongoing investment in maintenance and upgrades. The complexity and high operational costs act as a deterrent for potential competitors looking to enter or expand in this market.
Established Manufacturing Expertise
TSMC has developed a highly sophisticated manufacturing process that spans multiple intricate steps beyond lithography, such as wafer preparation, etching, doping, metallization, and packaging. Coordinating and optimizing these processes require deep expertise and experience, which TSMC has accumulated over decades. This expertise is not easily replicated, giving TSMC a significant operational advantage.
Customer Trust and Relationship
TSMC serves major semiconductor companies that design cutting-edge chips. These customers value reliability, quality, and consistency in production, factors that TSMC has proven itself capable of delivering. Switching foundries involves substantial risk and disruption, which makes customers reluctant to change suppliers unless there is a compelling reason. TSMC's long-standing relationships and reputation as a dedicated foundry further strengthen its moat.
Limited Competition at TSMC's Level
In the advanced semiconductor manufacturing space, TSMC faces limited direct competition. Samsung is its closest competitor, but both companies dominate due to their immense scale, technological prowess, and financial strength. This duopoly, with TSMC as the leading dedicated foundry, further consolidates its position in the market.
Investment Theses
TSMC stands out as an industry leader for its production of cutting-edge technology.
TSMC has consistently prioritized the development of robust, internal R&D capabilities. As a prominent leader in global semiconductor technology, TSMC offers the most cutting-edge and extensive range of dedicated foundry process technologies. In 2022, TSMC initiated high-volume production of its 3nm FinFET (N3) technology, representing the industry's most advanced semiconductor technology with superior power, performance, and area (PPA) compared to its 5nm predecessor.
TSMC has introduced advanced versions of its N3 technology, including N3E and N3P, aimed at enhancing power, performance, and density. N3E began mass production in late 2023, and TSMC plans to further expand its 3nm technology family with N3X for high-performance computing and N3AE for automotive applications.
Increased US restrictions on China's access to advanced chip technology and Samsung's challenges with 3nm GAA yield rates have highlighted TSMC's dominant position. Major tech firms like NVIDIA, AMD, Intel, Qualcomm, MediaTek, Apple, and Google are shifting to TSMC's 3nm process despite rising prices.
Concurrently, TSMC is also developing its 2nm (N2) technology, featuring nanosheet transistors, with volume production expected in 2025. This new technology aims to set industry benchmarks in density and energy efficiency, reinforcing TSMC's leadership in semiconductor technology.
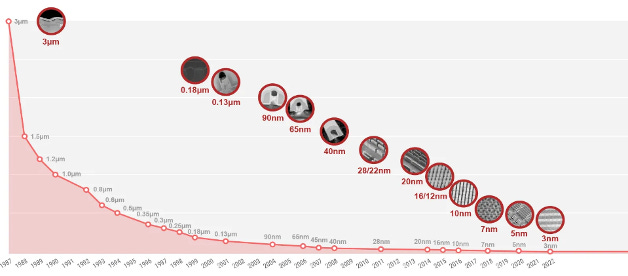
Figure 3 above shows the rapid development of smaller chips in recent years, emphasizing the continuous need to innovate.
TSMC's role as the largest pure-play foundry allows it to collaborate with both IDMs and design houses.
Although Broadcom operates as an IDM, it is also a customer of TSMC. Broadcom's AI-related revenue is expected to more than triple in the next few years, increasing from $4.2 billion in 2023 to $14 billion in 2025, accounting for 39% of the company's total semiconductor revenue. As one of the largest customers of TSMC, Broadcom's growth in AI-related revenue will benefit TSMC substantially.
To maintain its competitive edge in manufacturing chips with high performance yield, TSMC continues to invest heavily in R&D, spending $5.856 billion in 2023. This investment surpasses that of Broadcom, which spent $5.253 billion, and Samsung, which invested $2.273 billion.
The US Chips Act provides financial support to TSMC as it invested over $65 billion into three new chip factories in Arizona.
In a bid to attract semiconductor manufacturing back to the United States after its share of global chip fabrication capacity declined from about 40% in 1990 to around 12% in 2020, the Creating Helpful Incentives to Produce Semiconductors and Science Act of 2022 (the "U.S. CHIPS Act") offers financial incentives aimed at fostering the growth of the semiconductor industry within the United States.
In April 2024, TSMC announced today that the U.S. Department of Commerce has entered into a preliminary memorandum of terms (PMT) with TSMC Arizona, outlining potential direct funding of up to US$6.6 billion under the CHIPS and Science Act. Concurrently, TSMC revealed plans to construct a third fabrication facility at its Arizona site to meet robust customer demand, utilizing the most advanced semiconductor process technology available in the United States.
Therefore, the CHIPS and Science Act facilitates an unprecedented investment opportunity by enabling TSMC to provide cutting-edge manufacturing capabilities within the United States. TSMC’s operations in the United States will strengthen support for American customers, including leading global technology firms, and enhance its ability to drive future innovations in semiconductor technology.
Valuation
These peer companies were chosen as they are either foundries or as they that manufacture semiconductors. However, most of the peer companies are much smaller than TSMC with only Broadcom Inc. being of a comparable size. It is also notable that 40% of the growth comes from the top 4 largest semiconductor companies, namely Nvidia, TSMC, Broadcom and Qualcomm. Given that the larger cap companies experience a higher EV/LTM Sales, I took the best case scenario to forecast TSMC’s revenue.
I recommend a HOLD for TSMC, setting a 1 year price target of $27.88, and a 5 year price target of $48.59. Given that TSMC is slightly inflated after riding on the exponential revenue growth experienced by Nvidia, TSMC’s stock price could take a hit in 2024. However, I believe that the stock price will rebound in subsequent years due to the investment theses mentioned above.
Investment Risks and Mitigations
Geopolitical Tensions – The significance of Taiwan's semiconductor industry, particularly TSMC, lies not just in its economic value, but also in its strategic importance in the context of China-Taiwan relations. If China were to invade Taiwan and capture TSMC, along with its crucial extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUV) machines, it would face inevitable economic sanctions targeting the broader silicon supply chain, which would incentivize China to intensify its efforts to advance its own chipmaking capabilities to become a semiconductor superpower. To prevent China from invading, there could be a possibility of self-destruction of the key nodes of the semiconductor industry to prevent China from gaining access to TSMC’s EUV machines and semiconductor foundries.
Unable to keep up with demand – Due to the cyclical nature of the electronics and semiconductor market, the demand for electronics and semiconductors undergoes significant fluctuations. This volatility can affect TSMC's semiconductor foundry business, leading to revenue and earnings instability. Periods of industry downturns and overcapacity may reduce demand for TSMC's services, impacting its revenue, margins, and earnings. Failure to implement cost reduction measures during such downturns could exacerbate these challenges. Therefore, TSMC invested $5.856 billion on R&D in 2023 to develop the 2nm nodes, to improve performance and chip yield, and to increase production readily. This amounts to 8.5% of its revenue, matching or surpassing that of many other top high-tech companies
Volatility of exchange rates – With most of its operations and customer base located in US (68%), TSMC’s profit margin is affected by the exchange rate between TWD USD. However, the volatility of exchange rate has been low and TSMC used derivatives, currency forwards, and cross country swaps to hedge against exchange rate risk.
High customer concentration – In 2021, around 26% of its total revenue comes from Apple alone. In 2024, Nvidia is estimated to account for about 10% of TSMC’s revenues for 2024, as TSMC serves as the exclusive manufacturer for Nvidia's advanced AI training chips. This underscores that majority of the tech giants procure their chips from TSMC, ensuring that TSMC will benefit regardless of which company leads the market, mitigating the risk associated with high customer concentration.
Need for ultra-pure water – Despite its ample rainfall, Taiwan faces the threat of water shortages driven by climate change, which poses a significant risk to the semiconductor manufacturing industry. Semiconductor manufacturing remains heavily reliant on water-intensive processes due to the need for ultrapure water. TSMC's recycling efforts, including techniques like electrowinning, have achieved close to a 90% process water recycling rate, ensuring continuity despite Taiwan's low rainfall and stricter water regulations.
Despite TSMC's annual investment of $25 million in water reduction and recycling, achieving a one-third reduction in net water usage per chip compared to U.S. counterparts, further reductions have stalled, posing challenges such as lower production. TSMC has partnered with the Taiwanese government to invest in wastewater reuse plants and could consider additional measures like ocean water purification or building fabs outside Taiwan with water conservation in mind. Production interruptions due to water rationing could have severe long-term business implications, especially with China investing heavily in domestic semiconductor production.
ESG Consideration
Poor minority representation among executives – There is insufficient female representation among the executives, with only 2 out of 27 being women, and a lack of diversity as all executives are Chinese. However, the Board of Directors has adequate representation with 2 out of 10 of the board members being women. The board members comprise citizens of Taiwan, Europe, and the U.S., and possess world-class corporate management experience. 7 out of 10 of the directors are independent, which means that there are no marital or second-degree kinship relationships among the directors.
Concerns regarding the procurement of ultrapure water in terms of environmental sustainability – The semiconductor industry relies heavily on ultrapure water to clean silicon wafers, which later become computer chips. Although the ultrapure water starts extremely clean, it picks up residual chemicals and particles from the wafer surfaces during rinsing and end up in the industrial waste treatment system of the manufacturing facility. Semiconductor plants typically combine rinse water with acid waste in just two drain systems, making it difficult to reuse the rinse water without risking contamination and manufacturing defects. Consequently, ultrapure water is rarely recycled in semiconductor applications and is instead reclaimed for other uses.
Conclusion
To conclude, TSMC has established itself as a global leader in the semiconductor industry with strong fundamentals. It has strategically built fabrication plants in the US to benefit from government regulations and continues to invest heavily in R&D to maintain its technological leadership. Although cost drivers, US-China trade restrictions, and China-Taiwan relations could pose challenges, I believe TSMC has taken adequate measures to remain competitive.
*Do note that all of this is for information only and should not be taken as investment advice. If you should choose to invest in any of the stocks, you do so at your own risk.
References
TSMC's fate will indeed be at stake if China attacks Taiwan - Nikkei Asia
The Role of Ultra Pure Water in the Semiconductor Industry (lotusworks.com)
2 charts show how much the world depends on Taiwan for semiconductors (cnbc.com)
Semiconductor Market Size, Share, Growth & Forecast [2032] (fortunebusinessinsights.com)
3nm Technology - Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited (tsmc.com)
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company - statistics & facts | Statista
Top semiconductor companies by market cap 2024 | Statista
TSMC: Widest Moat in Semiconductor Stocks - by Oguz Erkan (capitalist-letters.com)
Nvidia (NVDA) Enters Correction Territory as Slump Erases $400 Billion - Bloomberg
Executives - Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited (tsmc.com)
Feature: What are the long-term costs... - Mobile World Live
https://www.chosun.com/english/industry-en/2024/06/18/SWLS2QOL2NEH3KRHYWGPSVAPU4/











Thanks Calista.
I have a few questions and would love to hear your thoughts!
Given the growing geopolitical tensions, particularly around Taiwan, how resilient is TSMC’s business model in the event of political instability or potential conflict in the region?
How diversified is TSMC’s customer base, and what is the risk associated with high customer concentration, especially with key players like Apple and Nvidia?
What specific market conditions or events would make you consider revising your "Hold" position on TSMC?
Thanks Calista, I do have some questions:
How far behind is Samsung in its 3nm process? Can we expect them to catch up with TSMC anytime soon?
Any thoughts on TSMC’s ability to continue purchasing these high-priced machines from ASML?
Based on valuation, it seems like the stock is well-priced today. Any expectations for correction?