Initial Report: LVMH (NYSE: LVMH), 37% 3-yr Potential Upside (VIP, Claire CONTRI)
Claire presents a "BUY" recommendation based on its unparalleled portfolio of iconic brands, strong financial performance, and strategic market positioning.
LinkedIn: Claire Giuffra Contri
1. Executive Summary
The following investment memo outlines an opportunity for LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton, a prestigious and globally renowned company commonly known as LVMH. LVMH, a leader in the luxury goods market, presents an investment opportunity that is both compelling and promising.
The global luxury market reached new heights in estimates, which suggests it hit a record value of €1.5 trillion (USD 1.63 trillion) in 2023. This represents an impressive growth of 8% to 10% compared to 2022. It is estimated to reach a CAGR of 3.22% between 2024 and 2028, while its market size is forecasted to reach USD 392.40 billion by 2030. This signifies growth from USD 272.74 billion in 2022. Fueled by a surge in demand from affluent millennials and Gen Z, the luxury sector is booming. Four key trends drive this growth: the digital transformation of the luxury world, the rise of luxury consumption in emerging markets, a growing appreciation for quality and sustainable fashion, and a shift in what defines luxury for younger generations.
Within the luxury market, LVMH stands out as a leading global powerhouse. Its success is built on a portfolio of iconic Maisons, each with a unique heritage and strong brand identity. LVMH fosters entrepreneurship and creativity within these “Maisons” (houses, in French), allowing them to adapt to new trends while staying true to their legacy. The group also provides its Maisons with shared resources and expertise, allowing them to operate efficiently and deliver exceptional products and experiences to customers around the world. LVMH's commitment to long-term vision and craftsmanship ensures its Maisons remain at the forefront of luxury for generations to come.
LVMH boasts a solid financial position, consistently ranking among the world's most valuable companies. This is reflected in its impressive market capitalization (USD 403,30 Billion in 2023). Additionally, the company maintains a healthy balance sheet with a low debt-to-equity ratio (18.56% in 2023). LVMH's focus on long-term profitability is further demonstrated by its favorable valuation metrics. These factors contribute to LVMH's ability to invest in future growth and deliver value to shareholders.
Hence, LVMH presents a compelling investment opportunity in the dynamic luxury market. The company's unique value proposition lies in its ability to:
Capitalize on emerging trends: LVMH actively explores new technologies and consumer preferences to stay ahead of the curve.
Pursue strategic acquisitions: The company has a proven track record of acquiring high-growth brands that complement its existing portfolio.
Optimize operations: LVMH continuously streamlines its business to deliver exceptional customer value.
While all investments carry some level of risk, LVMH offers a strong risk-reward profile. The company's focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles mitigates potential risks and aligns with investor values. Furthermore, LVMH boasts a diversified brand portfolio, a healthy balance sheet, and a long history of success, all contributing to its stability and growth potential.
In conclusion, LVMH represents a well-positioned investment in a thriving industry, offering the potential for significant long-term returns.
2. Company Overview
LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton SE, commonly known as LVMH, is a global powerhouse renowned for luxury, innovation, and superior craftsmanship. Formed in 1987 through the merger of Louis Vuitton and Moët Hennessy, this French conglomerate has become synonymous with opulence across various industries. With a prestigious portfolio encompassing over 70 prestigious brands in fashion, leather goods, perfumes, cosmetics, watches, jewelry, and spirits, LVMH sets the standard for luxury living. Through a steadfast commitment to excellence and a relentless pursuit of creativity, LVMH continues to captivate discerning consumers worldwide, elevating the art of luxury with its iconic brands and unwavering dedication to quality and sophistication.
2.1 Company History
2.1.1 Origins of Louis Vuitton and Moët Hennessy
Before consolidating into a single entity, three distinguished brands operated autonomously: Louis Vuitton, Moët & Chandon, and Hennessy.
Louis Vuitton: In the streets of Paris in 1854, Louis Vuitton founded his namesake brand, Louis Vuitton Malletier, at 33. His vision was to revolutionize travel by creating lightweight, airtight, and flat-topped trunks, departing from the rounded designs of his contemporaries. Vuitton's commitment to innovation and quality craftsmanship quickly earned him the patronage of Europe's elite, solidifying Louis Vuitton as a symbol of luxury and sophistication.
Moët & Chandon: The history of Moët & Chandon dates back to 1743 when Claude Moët established the winery in Epernay, France. Over the years, the champagne house became synonymous with celebrations, with its fine wines gracing the tables of royalty, aristocrats, and luminaries across the globe. The mastery of vineyard management, blending techniques, and savoir-faire elevated Moët & Chandon to unparalleled heights, setting the standard for luxury champagne.
Hennessy: Founded by Richard Hennessy in 1765, Maison Hennessy embarked on a journey to produce the world's finest cognacs. Nestled in the heart of the Cognac region, the House of Hennessy combined tradition, innovation, and a relentless pursuit of excellence to craft exceptional spirits. Through meticulous distillation, aging, and blending processes, Hennessy's cognacs captured the essence of French savoir-faire, captivating connoisseurs and enthusiasts worldwide.
2.1.2 The Merger and Formation of LVMH
The 1987 merger of Louis Vuitton and Moët Hennessy marked a watershed moment in the history of luxury. Louis Vuitton's reputation as a fashion and luxury luggage pioneer perfectly complemented Moët Hennessy's esteemed heritage in wines and spirits. This strategic alliance created LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton SE, a conglomerate with unparalleled expertise across multiple luxury market sectors. By leveraging synergies between fashion, leather goods, and beverages, LVMH positioned itself as a formidable force, poised to dominate the global luxury landscape.
2.1.3 Expansion and Acquisition
Under the dynamic leadership of Bernard Arnault, LVMH embarked on a relentless pursuit of growth through strategic acquisitions. Recognizing the value of iconic brands with rich histories and loyal followings, LVMH expanded its portfolio by acquiring prestigious names in fashion, jewelry, cosmetics, and more. These acquisitions included renowned fashion houses such as Givenchy, Fendi, and Celine and luxury watchmakers like TAG Heuer and Bulgari. Each addition to the LVMH family brought a unique heritage and craftsmanship, enriching the conglomerate's offerings and further solidifying its dominance in the luxury market.
2.1.4 Global Influence and Innovation
As the 20th century progressed, LVMH's influence extended far beyond its native France, reaching every corner of the globe. The conglomerate's brands became symbols of luxury and sophistication, coveted by discerning consumers worldwide. LVMH's commitment to innovation drove the development of groundbreaking designs, cutting-edge technology, and sustainable practices. From pioneering fashion trends to revolutionizing winemaking techniques, LVMH continually pushed the boundaries of luxury, setting new standards of excellence for the industry. Through strategic partnerships, immersive brand experiences, and digital innovation, LVMH cemented its position as a global leader, shaping the future of luxury for generations to come.
2.1.5 Continued Success and Legacy
Today, LVMH is the undisputed leader in the luxury goods market, with a vast portfolio encompassing over 70 prestigious brands. Despite the industry's ever-changing landscape, LVMH remains steadfast in its commitment to quality, creativity, and sustainability. The conglomerate's enduring success is a testament to its ability to evolve with the times while staying true to its founding principles. As LVMH charts its course into the future, its rich heritage, innovative spirit, and unwavering dedication to luxury ensure that its legacy will endure for years to come, shaping the world of luxury for generations to come.
3. Business Segments
LVMH operates under six distinct business segments, each catering to a specific area of the luxury market:
Fashion & Leather Goods: LVMH's largest and most historic segment, encompassing iconic brands like Louis Vuitton, Fendi, Givenchy, Celine, Loewe, and Kenzo. It focuses on high-end clothing, handbags, luggage, and other leather accessories.
Wines & Spirits: This segment houses some of the world's most prestigious beverage brands, including Moët & Chandon, Hennessy, Dom Pérignon, Glenmorangie, and Krug. It encompasses champagne, cognac, whiskey, and other premium spirits.
Perfumes & Cosmetics: This segment features renowned beauty brands like Christian Dior Perfumes & Cosmetics, Guerlain, Givenchy Beauty, Benefit Cosmetics, Fenty Beauty by Rihanna (developed in a partnership with singer Rihanna), and Make Up For Ever. It offers fragrances, makeup, skincare, and other beauty products.
Watches & Jewelry: This segment houses luxury watches and jewelry brands like Bulgari, Tag Heuer, Chaumet, Hublot, Zenith, and Fred. It caters to high-end timepieces and exquisite jewelry pieces.
Selective Retailing: This segment primarily includes Sephora, the world's leading beauty retailer known for its extensive brand selection and curated shopping experience. DFS, a global leader in airport duty-free retail, also falls under this segment.
Other Activities: This segment encompasses various businesses that must neatly fit into the different categories. It includes LVMH's publishing arm, Les Echos-Le Parisien Group, which owns several French newspapers.
Figure 1
LVMH's revenue breakdown reveals a clear leader: Fashion and Leather Goods, accounting for a whopping 73.84% in 2023. This segment houses iconic brands like Louis Vuitton and Fendi, solidifying LVMH's position as a powerhouse in luxury apparel and accessories.
Watches and Jewelry (9.48%) and Wines and Spirits (9.25%) follow closely behind, showcasing LVMH's diverse portfolio. Brands like Bulgari and Hennessy within these segments contribute significantly to the company's success.
Selective Retailing (6.10%), primarily driven by Sephora, demonstrates the importance of LVMH's curated shopping experiences. Perfumes and Cosmetics (3.13%) and Other Activities (1.79%) are rounding out the picture, highlighting LVMH's reach across various facets of the luxury market.
Figure 2
LVMH's Global Reach:
Looking beyond borders, LVMH's revenue streams paint a picture of a truly global company. Asia leads the pack with a significant 31% contribution, showcasing the growing luxury market in the region. The US is just a little behind at 25%, reflecting the enduring appeal of luxury goods for American consumers. Meanwhile, Europe remains a key market at 17%, with France (8%) and Japan (7%) contributing their own share. LVMH's diverse geographic footprint ensures stability and growth across different economic climates.
Currencies of Luxury:
Interestingly, when it comes to the currency used for transactions, LVMH sees a strong presence of "other currencies" (42%). This reflects the company's global reach and ability to cater to diverse customer preferences. However, established currencies still play a significant role: the US Dollar remains important (28%), followed by the Euro (20%), the Japanese Yen (7%), and the Hong Kong Dollar (3%). This mix highlights the international nature of the luxury goods market.
Now, let’s examine each segment of LVMH more thoroughly and explain why it represents a good investment opportunity.
3.1 Fashion & Leather Goods Segment
The Fashion & Leather Goods business group comprises brands with rich histories and a legacy of exceptional craftsmanship. While respecting these brands' identities and autonomous management, LVMH supports their growth by providing shared resources. This segment comprises a prestigious portfolio of Maisons, each with a unique heritage and brand identity. The Fashion & Leather Goods segment represented €42.169 million of LVMH's revenue in 2023. Here's a comprehensive overview of this segment:
Market Leadership: At the heart of LVMH's Fashion & Leather Goods segment are its iconic brands, each celebrated for its distinctive style, heritage, and craftsmanship. These brands include Louis Vuitton, Christian Dior, Fendi, Celine, Loewe, Kenzo, and Marc Jacobs. Each brand embodies luxury and sophistication, commanding a loyal following of discerning consumers worldwide.
Diversified Portfolio & Heritage: LVMH offers a diverse range of styles and price points within the Fashion & Leather Goods segment. This caters to a broader customer base and mitigates risk by not relying solely on one brand or trend. Furthermore, LVMH's Fashion & Leather Goods brands boast rich histories and a legacy of exceptional craftsmanship. From Louis Vuitton's heritage in luxury travel trunks to Christian Dior's haute couture legacy, these brands showcase a commitment to quality, innovation, and attention to detail. Skilled artisans and craftsmen employ traditional techniques and the finest materials to create timeless pieces that exude elegance and refinement.
Focus on Innovation: While steeped in tradition, LVMH's Fashion & Leather Goods brands also embrace innovation and creativity. These brands continually push the boundaries of fashion and design, introducing innovative silhouettes, materials, and techniques that resonate with modern consumers. For example, LVMH invests in technological advancements and sustainable practices within its Maisons. This ensures efficient production, reduces environmental impact, and aligns with today's luxury consumer values. From avant-garde runway collections to iconic handbag designs, LVMH's brands set trends and shape the fashion landscape.
In conclusion, LVMH's Fashion & Leather Goods segment offers a compelling investment opportunity. Its combination of market leadership, brand diversification, and innovative approach positions the segment for continued growth and strong financial performance.
3.2 Wines & Spirits Segment
LVMH boasts an unparalleled collection of iconic wine and spirit estates. These Maisons, some dating back centuries, are all deeply rooted in the world's most prestigious wine appellations and terroirs. This sector accounted for €6.60 million of LVMH's revenue in 2023. Here's a deeper dive into this segment:
Brand Power: LVMH enjoys leadership in the premium beverage market. The Wines & Spirits segment is home to some of the world's most renowned wine and spirits brands, each with a rich heritage and distinctive character. These brands include Moët & Chandon, Dom Pérignon, Veuve Clicquot, Krug, Hennessy, Glenmorangie, and Belvedere. These brands are celebrated for their exceptional quality, craftsmanship, and timeless appeal.
Legacy & Terroir: LVMH's Wines & Spirits segment boasts a unique advantage: a collection of estates steeped in history and deeply rooted in prestigious wine appellations and terroirs. This heritage translates to exceptional quality and exclusivity, further strengthening brand value and consumer desire.
Diverse Portfolio: LVMH's Wines & Spirits portfolio encompasses a wide range of products, including champagne, cognac, whiskey, vodka, tequila, and other spirits. This diverse portfolio allows LVMH to cater to a broad spectrum of consumer preferences and occasions, from celebratory moments with champagne to leisurely sipping premium spirits.
Innovation & Expertise: While rooted in tradition and heritage, LVMH's Wines & Spirits brands embrace innovation and creativity. LVMH invests in winemaking techniques and distribution strategies within its Maisons. This ensures efficient production, maintains exceptional quality standards, and allows the company to adapt to evolving consumer preferences. LVMH's expertise in brand management further strengthens the segment's position. For example, in 2023, LVMH bolstered its position in the high-quality rosé market with the acquisition of Château Minuty, which holds the prestigious Cru Classé des Côtes-de-Provence designation.
LVMH's Wines & Spirits segment is exposed to a leader in the premium beverage market. The segment boasts strong brand power, operates in a resilient and growing demand, and leverages a rich heritage to deliver exceptional products. With LVMH's commitment to innovation and expertise, this segment presents a compelling opportunity for long-term growth and value creation.
3.3 Perfumes & Cosmetics Segment
LVMH is a key player in the perfume, makeup, and skincare sector, with a portfolio of world-famous French brands. Hence, this segment exposes investors to the ever-evolving beauty world, a dynamic market driven by innovation and consumer desire. This sector represented €8.27 million of revenue in 2023. Here's a closer look at this segment:
Prestigious Brands: LVMH's Perfumes & Cosmetics segment is home to an impressive array of iconic brands, each renowned for its quality, innovation, and luxury. Some of the segment's flagship brands include Christian Dior, Givenchy, Guerlain, Fenty Beauty by Rihanna, and Benefit Cosmetics. These brands cater to diverse consumer preferences, offering a wide range of fragrances, skincare products, makeup, and beauty accessories.
Innovation & Trendsetting: The beauty landscape constantly evolves, and LVMH understands the importance of staying ahead. Its Maisons actively invest in research and development, creating innovative products and capitalizing on emerging trends. This ensures the segment remains relevant and exciting for beauty enthusiasts.
Omnichannel Strategy & Retail Expertise: LVMH leverages a powerful omnichannel strategy, offering products online and through its extensive network of retail stores, including Sephora, a global leader in beauty retail. This ensures maximum reach and caters to diverse customer preferences. LVMH's expertise in retail management further strengthens the segment's ability to deliver exceptional customer experiences and drive sales.
Overall, LVMH's Perfumes & Cosmetics segment enables exposure to a leader in the dynamic beauty market. The segment boasts a strong brand portfolio, operates in a resilient and growing market, and prioritizes innovation to stay ahead of trends. With LVMH's omnichannel strategy and retail expertise, this segment offers compelling growth and value-creation opportunities.
3.4 Watches & Jewelry
The LVMH Watches & Jewelry Maisons are some of the most emblematic brands in the industry. They operate in jewelry and watches. A daily quest for excellence, creativity, and innovation guides these Maisons. This segment caters to a sophisticated clientele seeking exquisite craftsmanship and timeless pieces. This sector represented €10.90 million of LVMH's revenue in 2023. Here's a deeper look into this segment:
Brand Legacy: LVMH's Watches & Jewelry segment is home to several iconic brands with rich history and distinctive styles. These brands include TAG Heuer, Hublot, Bulgari, and Chaumet. Each brand brings unique expertise and creativity to the segment, catering to diverse consumer preferences and tastes. These Maisons boast a rich heritage and unparalleled watchmaking and jewelry design expertise. This strong brand legacy translates to enduring customer loyalty and a reputation for exceptional quality, ensuring consistent demand and pricing power.
Global Reach: LVMH's Watches & Jewelry brands have a solid international presence, with boutiques and retail partners in key global markets. These brands are renowned for their exclusivity and prestige, attracting discerning consumers seeking luxury and sophistication.
Innovation & Relevance: While tradition is key, LVMH understands the importance of staying relevant. Its Maisons continuously innovate, incorporating new materials and techniques while staying true to their heritage. This ensures the segment caters to modern tastes while preserving the timeless appeal of luxury watches and jewelry.
Overall, LVMH's Watches & Jewelry segment offers exposure to a leader in a growing market. The segment boasts a powerful brand legacy, caters to an increasing demographic, and provides the potential for capital appreciation. With LVMH's commitment to innovation, this segment presents a compelling opportunity for long-term growth and value creation.
3.5 Selective Retailing
LVMH's reach extends beyond its prestigious brands. LVMH's Selective Retailing segment encompasses a portfolio of luxury retail outlets that offer curated selections of high-end products to discerning consumers. This segment, representing €17.88 million of LVMH's revenue in 2023, plays a significant role in the Group's overall operations, contributing to the conglomerate's diversified revenue streams and enhancing its brand presence in key markets worldwide. Here's a deeper look into some of the key components of LVMH's Selective Retailing segment:
DFS Group: DFS Group is a leading travel retailer offering duty-free luxury goods in airports, downtown locations, and resorts worldwide. Focusing on exceptional customer service and unique shopping experiences, DFS Group caters to affluent travelers seeking luxury products from renowned brands. The company's extensive network of stores spans major international travel destinations, making it a key player in the global luxury travel retail market.
Sephora: Sephora is a premier beauty retailer known for its extensive selection of prestige cosmetics, skincare, and fragrance brands. With a strong emphasis on innovation and customer experience, Sephora offers immersive shopping experiences both in-store and online, attracting beauty enthusiasts seeking the latest trends and products. The brand's strategic partnerships, exclusive product offerings, and innovative marketing initiatives have solidified its position as a global beauty retail industry leader.
Le Bon Marché: Le Bon Marché is a historic department store in Paris, France, renowned for its curated selection of luxury fashion, home goods, and gourmet food products. Focusing on art, culture, and lifestyle, Le Bon Marché offers a unique shopping experience celebrating Parisian elegance and sophistication. The store's iconic architecture, exclusive collaborations, and cultural events attract visitors worldwide, making it a must-visit destination for luxury shoppers in Paris.
La Samaritaine: La Samaritaine is an iconic department store in the heart of Paris. It offers a diverse range of luxury goods, including fashion, beauty, home décor, and gourmet food. After extensive renovation, La Samaritaine has been revitalized as a destination for luxury shopping and cultural experiences. The store's blend of heritage and modernity, coupled with its prime location on the banks of the Seine River, makes it a symbol of Parisian luxury and elegance.
Overall, LVMH's Selective Retailing segment encompasses a portfolio of prestigious brands and retail outlets that cater to affluent consumers seeking luxury products and experiences. Therefore, this segment offers exposure to a dominant player in the evolving retail landscape. Furthermore, it fosters brand exposure for the broader LVMH portfolio, creating a synergistic opportunity for growth and value creation.
3.6 Other Activities
LVMH's dominance extends far beyond its core business segments. The Other Activities Segment encompasses diverse ventures beyond its core luxury goods businesses, offering additional avenues for growth and revenue diversification. Here's a deeper look into some of the key components of this segment:
Selective Retailing: LVMH's selective retailing division includes a range of luxury retail outlets that offer curated selections of high-end products to discerning consumers. This includes department stores, duty-free shops, and multi-brand boutiques. Notable brands within this segment include DFS Group, Sephora, Le Bon Marché, and La Samaritaine. These retail destinations cater to affluent customers seeking unique shopping experiences and premium products across various categories, including fashion, beauty, and lifestyle.
Hospitality and Real Estate: LVMH invests in the hospitality and real estate sectors, focusing on luxury hotels, resorts, and residential properties. The company's Cheval Blanc brand, known for its exceptional service and exquisite accommodations, exemplifies its presence in the hospitality sector. LVMH's investments in high-end real estate properties further complement its luxury offerings, providing affluent clientele with exclusive living spaces and vacation destinations.
Other Ventures: LVMH's "Other Activities" segment may also include investments in media, entertainment, and technology ventures, although these are typically smaller in scale compared to its core businesses. These ventures may serve as strategic partnerships or investments in emerging industries that align with LVMH's brand positioning and long-term growth objectives.
While the "Other Activities" segment might not currently be a major revenue driver, it reflects LVMH's commitment to constant evolution and strategic thinking. Hence, this segment plays a vital role in expanding the company's footprint beyond traditional luxury goods, offering opportunities for diversification and innovation. By leveraging its expertise and resources across various industries, LVMH continues to explore new avenues for growth and value creation while maintaining its reputation as a global leader in the luxury market.
4. Industry Overview
4.1 Market Size
The global luxury market reached new heights in estimates, which suggests it hit a record value of €1.5 trillion (USD 1.63 trillion) in 2023. This represents an impressive growth of 8% to 10% compared to 2022. It is estimated to reach a CAGR of 3.22% between 2024 and 2028, while its market size is forecasted to reach USD 392.40 billion by 2030. This signifies growth from USD 272.74 billion in 2022. Fueled by a surge in demand from affluent millennials and Gen Z, the luxury sector is booming. Four key trends drive this growth: the digital transformation of the luxury world, the rise of luxury consumption in emerging markets, a growing appreciation for quality and sustainable fashion, and a shift in what defines luxury for younger generations.
4.2 Growth Drivers
4.2.1 Digital Transformation
Moreover, studies have predicted that online will soon surpass all other luxury sales channels, signifying a profound shift in consumer behavior and market dynamics. This transformation is driven by the growing preference for the convenience and accessibility of online shopping, especially among digital natives like Millennials and Gen Z, who value the seamless experiences offered by e-commerce. Advanced e-commerce platforms now provide sophisticated user experiences with high-resolution product images, detailed descriptions, and secure transactions, enhancing consumer trust and satisfaction. For instance, according to some research, the share of online sales for personal luxury goods will grow to 33% by 2033 (Figure 3). This shows how important enhancing the digital presence will be for luxury brands in the future.
Technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) bridge the gap between online and offline shopping, offering immersive experiences. AI-driven recommendation engines personalize shopping by analyzing consumer behavior. This technological transformation aims to create a more unique and enjoyable shopping experience.
Luxury brands leverage data analytics and social media for targeted advertising and influencer collaborations to reach and engage wider audiences. The direct-to-consumer (DTC) model eliminates intermediaries and allows brands to control pricing and customer experience while offering exclusive online collections. E-commerce also facilitates global market reach, enabling brands to enter emerging markets and tailor strategies to local preferences. The wealth of data from online sales empowers brands to make informed decisions and improve customer satisfaction, highlighting the significant impact of digital transformation in driving growth for the luxury industry.
Figure 3
4.2.2 A New Era of Consumers
In addition, the rise of Millennials and Generation Z as dominant consumer demographics significantly drives growth in the luxury industry. These cohorts, born between the early 1980s and the early 2010s, bring unique preferences and behaviors that reshape the luxury market. For instance, Millennials and Gen Z accounted for the entire growth of the global luxury market in 2022, according to Bain and Altagamma’s study. Indeed, both Millennials and Gen Z have grown up in a digital era, making them adept at online shopping and digital interactions. They prefer shopping on mobile devices and value the convenience and accessibility of e-commerce platforms. Luxury brands that invest in sophisticated online presences and mobile-optimized websites are better positioned to capture the attention of these tech-savvy consumers.
Similarly, social media plays a crucial role in the purchasing decisions of millennials and Gen Z. Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Snapchat are integral to their lives as they follow influencers, celebrities, and brands. Luxury brands that effectively leverage social media marketing collaborate with influencers, and create engaging and authentic content can build strong connections with these demographics. As a result, it is estimated that Gen Z and Alpha affluent consumers will make up 30% of the luxury market by 2030, growing three times faster than other generations (Figure 4).
Therefore, another important topic to discuss in the coming years is the next generation of ‘Alpha affluent consumers.’ One example of such consumers is Chinese consumers. They are still expected to drive a significant increase in luxury spending, projected to account for 40% of the global luxury market by 2030, down from the previously forecasted 50% by 2025, as reported by Bain & Co. Furthermore, other Asian countries, such as India and Indonesia, are witnessing a rise in wealth among their consumers. This shift is evident in luxury brands' strategies, such as Louis Vuitton appointing actress Deepika Padukone as its first Indian "House Ambassador" in May 2022, highlighting the brand's focus on the Indian market.
Figure 4
4.2.3 Sustainability and Second-hand Market Boom
Luxury goods companies have rebounded to pre-pandemic profitability levels and are also undergoing a significant transformation towards an environmentally responsible, circular economy business model. This shift is driven by customer demand and increasing regulatory pressure, and technology is crucial in accelerating this green transition.
Indeed, consumer demand for ethical practices is rising, especially among Millennials and Gen Z, who are increasingly prioritizing sustainability. They expect brands to demonstrate a genuine commitment to ethical practices, including environmentally friendly production methods, fair labor practices, and responsible materials sourcing. Hence, luxury brands are responding by adopting sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials, reducing carbon footprints, and ensuring transparency in their supply chains. For example, brands like Stella McCartney and Gucci have been at the forefront of sustainable luxury, integrating eco-friendly materials and processes into their products.
Moreover, in recent years, there has been a boom in the second-hand luxury market. Indeed, the rise of online resale platforms such as The RealReal, Vestiaire Collective, and Poshmark has facilitated the growth of the second-hand luxury market. These platforms offer a wide range of authenticated luxury items, providing consumers with a trustworthy and convenient way to purchase and sell pre-owned luxury goods. According to a report by Bain & Company, the second-hand luxury market is growing four times faster than the primary luxury market. This trend is expected to continue, with more consumers embracing the circular economy and the concept of e-commerce. In reaction to this trend, many luxury brands are now entering the second-hand market. For instance, Gucci has partnered with The RealReal to offer pre-owned items, and Burberry has launched its own resale platform. These initiatives allow brands to maintain control over their products’ secondary lifecycle and reinforce their commitment to sustainability.
Therefore, by participating in the second-hand market, brands can reach a broader audience, including younger consumers more inclined towards sustainable consumption practices. These brands can build stronger relationships with their consumers as ethical and sustainable practices resonate well with modern consumers, fostering brand loyalty and encouraging repeat purchases. They can also help make high-end goods accessible to a wider audience. This democratization of luxury can drive growth by tapping into new customer segments who value quality but are also price-sensitive and eco-conscious.
4.2.4 Focus on Personalization
Personalization is a powerful growth driver for the luxury industry, significantly transforming how brands engage with their consumers and enhancing the overall customer experience. Modern luxury consumers, particularly Millennials and Gen Z, seek unique, personalized products that reflect their individual tastes and preferences. Brands are responding by offering bespoke services, such as custom-made clothing and tailored beauty products while creating personalized shopping experiences through advanced technologies like AI and data analytics. These technologies allow brands to understand consumer preferences and deliver tailored recommendations, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) further revolutionize the shopping experience by allowing customers to try on products and explore customized designs virtually.
Moreover, effective personalized communication, through targeted messaging and content and personalized loyalty programs, fosters strong customer relationships and loyalty. Additionally, personalization allows luxury brands to cater to diverse markets and broaden their reach by tailoring offerings to meet the specific preferences of different consumer segments. This focus on personalization enhances the customer experience, drives innovation, and supports sustainable growth in the competitive luxury market.
Figure 5 clearly illustrates the key elements defining the 'new' luxury paradigm.
Figure 5
4.3 Competitor Analysis
The competitor analysis provides a deeper insight into LVMH’s competitive landscape and overall market positioning relative to other key players in the industry. The following section compares LVMH with its main competitors, highlighting selected ratios and performance metrics to illustrate their relative strengths and weaknesses.
Figure 6
4.3.1 Market Capitalization
Figure 6 illustrates a compelling observation regarding the market capitalizations of top competitors within the luxury goods sector. Notably, LVMH stands out prominently with the highest market capitalization recorded at €394.2 million. This figure underscores LVMH's formidable position within the industry, reflecting its robust financial performance, strong brand portfolio, and strategic market positioning.
LVMH's substantial market capitalization signifies its dominant presence in the luxury market and underscores investor confidence in the company's ability to generate sustainable growth and deliver value over the long term. This significant valuation places LVMH at the forefront of its peers, highlighting its resilience and adaptability in navigating dynamic market conditions and evolving consumer preferences.
Moreover, LVMH's commanding market capitalization speaks to its competitive advantage and strategic initiatives to drive innovation, expand into new markets, and nurture its luxury brand ecosystem. By consistently delivering exceptional products and experiences while staying true to its heritage and commitment to excellence, LVMH continues to solidify its position as a global leader in the luxury goods industry, setting a benchmark for its competitors to aspire to.
4.3.2 Revenues
In terms of revenue generation, LVMH once again demonstrates its industry dominance with a total revenue of €86.153 million. This impressive figure underscores the group's robust business model and ability to leverage a diverse portfolio of luxury brands across various sectors, including fashion, leather goods, perfumes, cosmetics, watches, jewelry, wines, and spirits.
LVMH's ability to consistently deliver high revenue also reflects its successful execution of targeted acquisitions and organic growth strategies. By integrating new and complementary brands into its portfolio while preserving their unique identities and autonomy, LVMH has enhanced its market reach and strengthened its competitive edge.
Furthermore, the group's emphasis on digital transformation and enhancing the customer experience through cutting-edge technologies has played a crucial role in driving sales and revenue. By optimizing its value chain and ensuring seamless integration from product conception to distribution, LVMH has maximized operational efficiencies and met the evolving demands of a discerning global clientele.
4.3.4 Enterprise Value (EV)
Furthermore, LVMH’s enterprise value (EV) stands out significantly, surpassing all its competitors by a substantial margin. With an EV of €406,164 million, LVMH's valuation is nearly double that of Hermès, triple that of Unilever, and quadruple that of Richemont. This exceptional enterprise value not only underscores LVMH's financial strength but also highlights its absolute dominance within the luxury goods sector.
The remarkable EV of LVMH reflects the market's confidence in the company's future growth prospects and its ability to generate substantial cash flows. It indicates a high level of investor trust in LVMH's strategic direction, management capabilities, and overall market positioning. This high valuation is a testament to the group's successful execution of its long-term vision, which includes a focus on innovation, brand diversification, and sustainable development.
In summary, LVMH’s enterprise value highlights its commanding position in the luxury goods sector and showcases its strategic prowess and ability to deliver exceptional value to shareholders. This dominance in EV is a clear indicator of LVMH's robust market standing and its potential for continued success and expansion in the future.
4.3.4 P/E and EV/EBITDA Ratio
Lastly, LVMH has an EV/EBITDA ratio of 14.13, which positions it competitively among its peers. To provide context, this ratio is a key financial metric used to assess a company's valuation. It compares the enterprise value (EV) to the earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), offering insights into a company's overall financial health and valuation efficiency.
For LVMH, an EV/EBITDA ratio of 14.13 suggests that investors are willing to pay 14.13 times the company's EBITDA for its enterprise value. When compared to its competitors, this figure provides a benchmark for evaluating LVMH's market valuation relative to its earnings:
Hermès: With an EV/EBITDA of 35.81, Hermès is valued much higher relative to its EBITDA. This indicates that investors see Hermès as having a very strong earnings potential or lower risk, justifying a higher multiple.
L’Oréal: At 24.89, L’Oréal's ratio is also significantly higher than LVMH's, suggesting that the market perceives L’Oréal's earnings potential or stability as superior to LVMH's.
Kering: Kering's ratio of 7.48 is notably lower, indicating that the market might view Kering as having a higher risk or lower growth potential compared to LVMH.
Prada: Prada’s EV/EBITDA ratio of 10.86 places it below LVMH, suggesting it might be seen as slightly less attractive in terms of growth potential or stability relative to LVMH.
LVMH's EV/EBITDA ratio of 14.13 indicates a balanced perception by investors. It reflects confidence in the company's profitability and growth prospects while considering its risk profile. This ratio, being lower than Hermès and L’Oréal, suggests that LVMH might be undervalued compared to these companies, potentially offering better investment value. Conversely, its higher ratio compared to Kering and Prada underscores LVMH's stronger market position and perceived stability.
In summary, the EV/EBITDA ratio helps investors compare LVMH's valuation efficiency to its competitors, highlighting LVMH's balanced and competitive market standing. This metric provides a snapshot of how LVMH is valued in relation to its earnings, indicating robust investor confidence and a solid financial foundation.
5. Investment Thesis
The investment thesis of LVMH (Louis Vuitton Moët Hennessy) revolves around its position as a global leader in the luxury goods industry and its ability to capitalize on the growing demand for luxury products worldwide. Here are some key aspects of LVMH's investment thesis:
5.1 A Strong Brand Portfolio
Figure 7
LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton SE, the world's leading luxury goods conglomerate, presents a compelling investment thesis centered around its unparalleled brand portfolio. This diverse collection spans fashion and leather goods, perfumes and cosmetics, watches and jewelry, wines and spirits, and selective retailing, mitigating risks and capitalizing on various market trends. The portfolio includes iconic brands like Louis Vuitton, Dior, Fendi, Guerlain, TAG Heuer, Moët & Chandon, and Sephora, each maintaining strong identities and deep customer loyalty, which supports premium pricing and market leadership. LVMH leverages synergies across its brands, sharing best practices in design, production, and marketing, while strategic acquisitions, such as Tiffany & Co., bolster its market position. This strength translates into robust financial performance, generating high revenues and profitability and ensuring continuous investment in innovation and expansion. Ultimately, LVMH's diverse and prestigious brand portfolio provides a solid foundation for sustained growth and competitive advantage, making it a highly attractive investment opportunity.
Moreover, LVMH is deploying a strategy focused on diversifying its brands and conquering new markets while remaining true to its heritage and commitment to excellence. By fostering a long-term vision, the group invests in innovation and sustainable development of its Houses, ensuring their growth and adaptability to luxury market trends.
Therefore, the synergy among its various brands enables LVMH to enjoy a unique position in the market, offering various high-end products that cater to the desires of a demanding international clientele. Moreover, LVMH emphasizes strengthening its leadership by integrating digital technologies to enhance the customer experience and optimize its value chain, from design to distribution. This strategic approach is complemented by a targeted acquisition policy to integrate new houses into the LVMH group portfolio while preserving their identity and autonomy, thus stimulating organic growth and accessing new market segments.
5.2 An Emphasis on Product Sustainability
LVMH integrates sustainability as a core component of its investment thesis. The group’s emphasis on sustainable practices not only aligns with growing consumer preferences for eco-conscious brands but also enhances its long-term profitability and resilience.
Circular Economy & Eco-Design Integration
First of all, LVMH actively embraces circular economy principles, aiming to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency throughout its value chain. By designing products with recyclability and durability in mind, the company extends the lifespan of its luxury goods. Moreover, LVMH explores innovative ways to repurpose materials and components, contributing to a closed-loop system where materials are reused or recycled rather than disposed of. For example, Louis Vuitton launched the ReBelle collection, which features handbags made from upcycled materials sourced from pre-existing LV bags. This initiative extends the lifespan of luxury items and promotes a circular economy model within the brand.
Second-Hand Market Initiatives
Secondly, recognizing the growing popularity of the second-hand luxury market, LVMH strategically engages with this sector. The company supports initiatives that promote the resale and revaluation of pre-owned luxury items, either through its own platforms or in collaboration with reputable partners. By encouraging consumers to buy pre-owned items or participate in resale programs, LVMH extends the lifecycle of its products and reduces the overall environmental footprint associated with luxury consumption. An instance of LVMH's support for the second-hand market is evident in Celine's decision to reintroduce the iconic Phoebe Philo Bag, first launched in the 2010s, to the resale market. Through reintroducing sought-after designs, Celine promotes the purchase of pre-owned items, fostering waste reduction and advancing a more sustainable consumer approach.
Supply Chain Sustainability
LVMH places a strong emphasis on ensuring sustainability across its entire supply chain. This includes responsible sourcing of raw materials, ethical labor practices, and reducing carbon emissions in transportation and logistics. By working closely with suppliers and implementing rigorous standards and certifications, LVMH strives to minimize environmental and social impacts associated with production processes. Additionally, the company invests in technology and innovation to enhance transparency and traceability within its supply chain, allowing for greater visibility into the origins and journey of its products. For instance, Bvlgari implemented an ethical sourcing program for its jewelry, ensuring that diamonds and precious metals are responsibly mined and sourced. By adhering to strict ethical and environmental standards, Bvlgari minimizes the negative impacts of mining operations on local communities and ecosystems.
5.3 Strategic Acquisitions
Figure 8
LVMH strategically leverages acquisitions as a key component of its investment thesis. Through targeted acquisitions, LVMH expands its brand portfolio, strengthens its market position, and drives long-term growth and profitability.
Indeed, LVMH strategically acquires luxury brands that complement its existing portfolio or offer strategic synergies. By diversifying its brand portfolio across different sectors, such as fashion, cosmetics, watches, and wines, LVMH mitigates risks and capitalizes on opportunities in various segments of the luxury market. In addition, strategic acquisitions enable LVMH to consolidate its market position and gain a competitive advantage. By acquiring established brands with strong brand equity and market recognition, LVMH enhances its global footprint and captures new customer segments. Acquisitions also provides access to new distribution channels and market segments, enabling LVMH to reach a broader audience and capitalize on emerging market trends.
Moreover, LVMH excels in integrating acquired brands into its business ecosystem while preserving their unique identities and heritage. The group leverages its operational expertise, marketing prowess, and financial resources to unlock synergies and drive value creation. By optimizing supply chains, streamlining operations, and implementing best practices, LVMH enhances the performance and profitability of acquired brands, maximizing return on investment. The group also invests in research and development to enhance product offerings, innovate new designs, and capitalize on emerging consumer trends. Additionally, LVMH leverages the expertise and creativity of acquired brands to drive innovation across its entire portfolio, fostering a culture of excellence and creativity.
Lastly, strategic acquisitions contribute to LVMH's financial performance and shareholder value. By expanding its brand portfolio and market presence, LVMH generates incremental revenue streams and enhances profitability. Furthermore, successful acquisitions strengthen investor confidence and drive shareholder returns, reinforcing LVMH's position as a top-tier investment in the luxury goods sector.
Here are examples of strategic acquisitions made by LVMH:
Tiffany & Co. (2020): LVMH acquired Tiffany & Co., one of the world's most iconic luxury jewelry brands, in a landmark deal valued at $15.8 billion. This acquisition expanded LVMH's presence in the high-end jewelry market and strengthened its position in the United States, while also providing opportunities for synergies and growth in other regions.
Belmond Ltd. (2019): LVMH acquired Belmond Ltd., a global collection of luxury hotels, trains, and river cruises, for $3.2 billion. This acquisition bolstered LVMH's presence in the luxury hospitality sector and complemented its portfolio of prestigious brands, including Louis Vuitton and Moët & Chandon, offering new opportunities for cross-brand collaborations and experiential luxury offerings.
Rimowa (2016): LVMH acquired Rimowa, a leading German luxury luggage manufacturer known for its high-quality aluminum and polycarbonate suitcases, in a deal estimated at €640 million. This acquisition expanded LVMH's presence in the travel and accessories market and provided innovation and brand development opportunities within the luggage category.
Christian Dior (2017): LVMH acquired the remaining shares of Christian Dior that it did not already own, in a deal valued at €12.1 billion. This acquisition consolidated LVMH's control over one of its most iconic fashion brands, providing greater operational flexibility and alignment of strategic objectives within the LVMH group.
Benefit Cosmetics (1999): LVMH acquired Benefit Cosmetics, a San Francisco-based beauty brand known for its quirky packaging and fun-loving approach to makeup, in a deal estimated at $500 million. This acquisition expanded LVMH's presence in the cosmetics industry and provided opportunities for growth in the mass-market beauty segment.
These examples highlight LVMH's strategic approach to acquisitions, which aims to enhance its brand portfolio, strengthen its market position, and drive long-term value creation for shareholders. Through targeted acquisitions, LVMH continues to expand its footprint in key luxury sectors and capitalize on emerging market trends, solidifying its position as a global leader in the luxury goods industry.
5.4 Digital Innovation
Lastly, LVMH prioritizes digital innovation as a core component of its investment thesis. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies and digital platforms, LVMH enhances customer engagement, optimizes operations, and drives long-term growth and profitability.
First of all, LVMH embraces digital transformation within its retail network, integrating online and offline channels to create a cohesive omnichannel experience. Through initiatives like click-and-collect, virtual try-on, and in-store digital activations, LVMH bridges the gap between physical and digital retail, catering to the evolving needs and preferences of modern consumers. Some LVMH brands, such as Bulgari, leverage augmented reality (AR) technology to enable virtual try-on experiences for jewelry and watches. Customers can use their smartphones to visualize how pieces will look on them before making a purchase, enhancing confidence and reducing returns. By investing in technologies like RFID, IoT, and augmented reality, LVMH enhances inventory management, improves operational efficiency, and elevates the overall retail experience. For instance, Sephora offers services like click-and-collect, where customers can order products online and pick them up in-store, blurring the lines between digital and physical retail.
Secondly, digital innovation plays a crucial role in product design and development at LVMH. By leveraging 3D modeling, digital prototyping, and additive manufacturing technologies, LVMH accelerates the product development cycle, reduces time to market, and fosters creativity and innovation. Moreover, digital tools enable LVMH to optimize supply chain management, minimize waste, and enhance sustainability across its brands.
Lastly, LVMH collaborates with leading technology companies, startups, and digital innovators to drive innovation and stay at the forefront of digital transformation. By fostering strategic partnerships and investing in emerging technologies, LVMH gains access to cutting-edge solutions and expertise, accelerating its digital initiatives and enhancing its competitive position in the market. For example, LVMH has partnered with Google Cloud to leverage its data analytics and machine learning capabilities to enhance customer insights and optimize business operations across its brands.
All in all, digital innovation is a cornerstone of LVMH's investment thesis, enabling the company to enhance customer experience, transform retail operations, innovate in product design and development, and make data-driven decisions. By embracing digital transformation and leveraging emerging technologies, LVMH reinforces its position as a leader in the luxury goods industry, driving long-term growth and profitability in an increasingly digital world.
6. Valuation
6.1 Financial Summary
As of 2023, LVMH reported impressive financial results, reflecting its dominant position in the luxury goods market. The company achieved a total revenue of €79.2 million, with significant contributions from its diverse business segments. The Fashion & Leather Goods segment, led by iconic brands like Louis Vuitton, Christian Dior, and Fendi, remains the largest revenue generator, contributing €42.16 million. The Perfumes & Cosmetics segment, including Dior, Guerlain, and Fenty Beauty, reported €8.27 million in revenue. In contrast, the Watches & Jewelry segment, driven by TAG Heuer, Bulgari, and Chaumet, brought in €10.9 million. The Wines & Spirits segment, featuring brands such as Moët & Chandon and Hennessy, added €6.6 million, and the Selective Retailing segment, which includes Sephora and DFS, contributed €17.88 million. Other activities accounted for €324 million in revenue.
Figure 9
LVMH's profitability was equally robust, with an operating profit of €22.5 million and a net profit of €15.9 million, demonstrating its luxury brands' efficiency and high margins. Geographically, the company saw strong growth across Asia (excluding Japan), the United States, Europe, and Japan, driven by high consumer demand and increased spending on luxury goods.
Figure 10
The company's financial position remains solid, with total assets of €143.694 million, total equity of €67.2 billion, and net debt of €10.7 million, ensuring substantial liquidity and financial stability. LVMH continues to reward its shareholders with increased dividends, which are supported by its strong earnings and cash flow generation.
Strategically, LVMH has been active in acquisitions, notably enhancing its portfolio with the acquisition of Tiffany & Co., strengthening its presence in the high-end jewelry market. The company's commitment to innovation and sustainability, along with its diversified business model, positions it well for sustained long-term growth and continued market leadership in the global luxury goods industry.
6.2 Stock Price Evolution
Over the past 12 months (April 2023-April 2024), LVMH stock has decreased by 1.23%. During this period, the LVMH share price fluctuated between the support level of 647 euros (shown in purple) and the resistance level of 888 euros (shown in yellow). LVMH stock moved within a downward channel in the third quarter of 2023 (shown in gray on the chart) but rose again at the beginning of 2024 following a strong earnings report and historically high margin levels.
The medium-term trend is positive for LVMH stock, with the 50-day moving average (shown in black on the chart) above the 100-day moving average (shown in red). The short-term trend for LVMH stock is also positive, with the 20-day moving average (shown in green on the chart) above the 50-day moving average. The MACD is positive and below its signal line, and the stochastic RSI is in the neutral zone.
Figure 11
Furthermore, in 2023, major stock markets experienced a buoyant period, witnessing significant gains with most flagship indices reaching all-time highs by December, despite the backdrop of an economic slowdown and heightened geopolitical risk. Among them, the CAC 40, representing the Paris stock exchange, saw a notable increase of 16.5%, though slightly trailing behind the Euro Stoxx 50 (up 19.2%) and the DAX (up 20.3%). US markets outperformed, with the S&P 500 and Nasdaq soaring by 24.2% and 43.4%, respectively.
The year started promisingly, particularly for luxury stocks following the relaxation of China's public health restrictions at the close of 2022. However, markets encountered significant volatility amidst global economic uncertainties, including persistent inflation, a slower-than-expected recovery in China, and a banking crisis in March. Relief came in late October with signs of inflation easing, hinting at potential central bank policy shifts towards monetary easing in 2024, which fueled a robust year-end rally in equity markets.
LVMH's share price also rebounded towards the end of the year, recuperating some lost ground to finish with a 7.9% increase, reaching €733.60. By December 31, 2023, LVMH boasted a market capitalization of €368 billion, solidifying its position as the most valuable company in the CAC 40 index.
Figure 12
6.3 Financial Ratios
Figure 13 presents a set of financial metrics for LVMH from 2022 to 2025, including actual data for 2022 and 2023 and estimated data for 2024 and 2025. Here's an analysis of each metric:
EV/Sales (Enterprise Value to Sales)
Dec '22A: 5.11
Dec '23A: 4.70
Dec '24E: 4.51
Dec '25E: 4.19
Analysis: The EV/Sales ratio is declining over the period, indicating that LVMH's enterprise value is decreasing relative to its sales. This could suggest that the market is valuing the company's sales less over time, or it could be due to increasing sales outpacing the growth in enterprise value.
EV/EBIT (Enterprise Value to Earnings Before Interest and Taxes)
Dec '22A: 19.25
Dec '23A: 17.75
Dec '24E: 17.15
Dec '25E: 15.59
Analysis: Similar to the EV/Sales ratio, the EV/EBIT ratio is also decreasing. This suggests the company's enterprise value is declining relative to its operating earnings, indicating potential undervaluation or higher expected future earnings growth.
EBIT/Interest Expense
Dec '22A: 55.02
Dec '23A: 23.43
Dec '24E: 35.47
Dec '25E: 48.64
Analysis: This ratio measures the company's ability to cover its interest expenses with its earnings before interest and taxes. The significant drop in 2023 indicates a decrease in this coverage ability, possibly due to lower EBIT or higher interest expenses. However, it is expected to improve significantly in the subsequent years, suggesting better financial health and higher profitability or lower interest expenses.
Total Debt/EBITDA
Dec '22A: 1.32
Dec '23A: 1.34
Dec '24E: -
Dec '25E: -
Analysis: The slight increase from 2022 to 2023 indicates a marginal rise in leverage, meaning the company’s debt is slightly higher than its earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. Data for 2024 and 2025 is not provided, but maintaining a low ratio is typically a sign of strong financial stability.
Price to Earnings (P/E)
Dec '22A: 28.02
Dec '23A: 25.90
Dec '24E: 24.60
Dec '25E: 22.27
Analysis: The declining P/E ratio indicates that the price investors are willing to pay for each euro of earnings is decreasing. This might suggest that investors expect slower growth in the future or that the stock is becoming undervalued.
Overall Summary
LVMH appears to maintain strong financial health, as indicated by the EBIT/Interest Expense ratio, which shows improving coverage over time. Both EV-based ratios (EV/Sales and EV/EBIT) and the P/E ratio are declining, potentially indicating that the stock is becoming less expensive or that future earnings growth is expected to moderate. The Total Debt/EBITDA ratio remains low and relatively stable, indicating that the company is not excessively leveraged. Overall, LVMH's financial metrics suggest a company becoming more efficient and potentially undervalued, with expectations of improved profitability and stable financial leverage.
Figure 13
6.4 Financial Forecasts
6.4.1 Income Statement
Figure 14
LVMH's forecasted income statement reveals a steady growth trajectory over the next few years. Sales are projected to increase from €86,153 million in December 2023 to €103,859 million by December 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) driven by consistent organic growth, which peaks at 8.33% in Q4 2024 before stabilizing around 7.84% by 2026. Gross income is expected to rise correspondingly, reaching €72,379 million by December 2026. EBITDA shows a similar upward trend, growing from €29,085 million in December 2023 to €34,702 million by December 2026, indicating effective cost management and operational efficiency. Despite increased depreciation and amortization expenses, EBIT and EBITA also show positive growth. Interest expenses are projected to decrease slightly, improving pretax income, which is set to reach €27,577 million by December 2026. Consequently, net income is forecasted to grow from €15,174 million in December 2023 to €19,528 million by December 2026, underscoring LVMH's strong financial health and ability to enhance shareholder value through sustained profitability and strategic growth initiatives.
6.4.2 Balance Sheet
Figure 15
The forecasted balance sheet metrics for LVMH indicate a strong financial position and continued growth in assets and equity. Current assets are expected to increase significantly from $43,710 million in December 2023 to $75,786 million by December 2026, driven by substantial rises in cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, and inventories. Total assets follow a similar upward trend, projected to grow from $143,694 million in December 2023 to $171,212 million by December 2026. This growth is underpinned by increased intangible assets and working capital, reflecting LVMH's expanding operational scale and market presence.
Current liabilities are forecasted to rise from $33,145 million in December 2023 to $34,416 million by December 2026, suggesting manageable increases in obligations relative to asset growth. Total debt is projected to fluctuate, peaking at $21,235 million in December 2024 before declining to $18,630 million by December 2026, indicating an effort to reduce leverage and strengthen the balance sheet. Net debt follows a similar pattern, reducing from $10,746 million in December 2023 to -$5,645 million by December 2026, highlighting an improvement in the company’s net cash position.
Shareholder equity is anticipated to rise substantially, from $61,017 million in December 2023 to $90,906 million by December 2026, reflecting retained earnings and potentially higher profitability. This increase in equity, alongside a growing asset base, suggests a robust financial foundation and enhanced shareholder value. Overall, these forecasted metrics indicate LVMH’s strong financial health, strategic debt management, and effective asset utilization to drive growth and profitability.
6.4.3 Cash Flow Statement
Figure 16
Regarding the forecasted cash flow statement, Figure 16 reveals a period of robust growth and stabilization following significant investments. Capital expenditures increased substantially from $4,969 million in 2022 to $7,478 million in 2023, indicating substantial investments in infrastructure or expansion plans before stabilizing around $5,894 million to $6,154 million in the forecasted years. Despite an initial decline in free cash flow from $12,829 million in 2022 to $10,922 million in 2023, a strong recovery is projected, with free cash flow expected to rise to $16,661 million in 2024 and further to $20,215 million by 2026, reflecting improved operational efficiency and profitability. Cash flow from operations is also expected to grow substantially, increasing from $17,833 million in 2022 to $18,400 million in 2023. It is projected to reach $28,581 million by 2026, indicating robust business operations and higher revenue generation. While cash flow from investing remains negative, reflecting continuous asset investments, the outflows decrease slightly in the forecasted years. Cash flow from financing remains consistently negative, indicating ongoing financial obligations, but stabilizes around -$10,238 million to -$10,876 million. Notably, significant share repurchases in 2022 and 2023 are absent in the forecasted years, suggesting a strategic shift towards retaining cash for other uses or completing the buyback program. Overall, LVMH appears well-positioned for continued financial health and growth in the coming years, supported by strong operational performance and strategic investments.
6.4.4 Per Share
Figure 17
The forecasted per-share metrics for LVMH indicate a positive outlook for the company's financial performance over the coming years. Earnings per share (EPS) are projected to grow steadily from 30.33 in December 2023 to 39.09 by December 2026, reflecting strong earnings growth. EPS excluding extraordinary items follows a similar trend, highlighting consistent core profitability. Dividends per share are expected to increase from 13.00 in December 2023 to 16.95 by December 2026, indicating a commitment to returning value to shareholders. Free cash flow per share shows significant improvement, rebounding from 19.64 in December 2023 to 42.56 by December 2026, underscoring the company's growing cash generation capabilities. Cash flow per share also demonstrates a positive trajectory, increasing from 42.42 in December 2023 to 52.06 by December 2026, signaling robust operational cash flow. Additionally, the book value per share is forecasted to rise substantially from 121.96 in December 2023 to 179.52 by December 2026, indicating a strengthening balance sheet and increasing net asset value per share. Overall, these metrics suggest that LVMH is on a path to sustained growth and financial health, with strong earnings, dividend growth, and cash flow generation.
6.4.5 Valuation Metrics
Lastly, Figure 18 provides a comprehensive forecast of various financial valuation metrics for LVMH from December 2022 through December 2026. Analyzing these key metrics gives us insights into the company's future financial health and market expectations.
Figure 18
Starting with the Price/Earnings (P/E) ratio, it measures how much investors are willing to pay per dollar of earnings. The P/E ratio begins at 24.3 in December 2022, peaks at 27.1 in March 2024, and then declines to 20.3 by December 2026. This initial rise, followed by a decline, suggests that while investor confidence in LVMH may initially increase, it is expected to taper off in the long run. Similarly, the Book Value (BV) Growth, which reflects the growth in LVMH’s net asset value, shows a consistent increase from 11.2 in December 2023 to 16.9 in December 2026, indicating a strengthening balance sheet.
Secondly, the PEG ratio remains at 0.0 throughout the period, suggesting either no growth estimates or a lack of projected earnings growth data. On the other hand, the Price/Operating Cash Flow (P/OCF) ratio decreased from 17.4 in December 2022 to 16.3 in December 2026. This indicates that LVMH is expected to generate more operating cash flow relative to its price over time, a positive sign of financial health. The Price/Book Value (P/BV) ratio starts at 6.0 in December 2022, peaks again at 6.0 in December 2025, and then slightly decreases to 5.7 in December 2026. This stability suggests that the market consistently values LVMH’s assets highly.
Further analyzing the company’s valuation concerning its cash flows, both the Price/Cash Flow (P/CF) and Price/Free Cash Flow (P/FCF) ratios show a decreasing trend from 18.6 in December 2022 to 14.9 in December 2026. This indicates improved cash flow generation relative to the company’s market price. The Enterprise Value (EV) metrics, including EV/EBITDA and EV/EBIT, measure the company's enterprise value relative to its earnings. EV/EBITDA peaks at 15.7 in March 2024 and then declines to 12.1 by December 2026. Similarly, EV/EBIT reaches 18.3 in March 2024 before decreasing to 14.2 by December 2026. These trends suggest that while enterprise value initially increases relative to earnings, it eventually stabilizes at a lower level, reflecting a more conservative market valuation in the long term.
Moreover, the EV/FCF shows a slight increase from 36.3 in December 2023 to 37.5 in March 2024, then decreases to 24.6 by December 2026. This decline suggests that LVMH’s free cash flow is expected to grow faster than its enterprise value, which is favorable for investors. Both Return on Assets (ROA) and Return on Equity (ROE) remain stable over the period, with ROA around 0.5% and ROE around 0.6%, indicating consistent profitability and efficient use of assets and equity. Operating Return on Assets (OROA) and Net Income Return on Shareholder Equity (NIROE) also remain stable, with OROA around 0.4% and NIROE around 0.3%, reflecting steady operational efficiency and net income returns relative to shareholder equity.
Lastly, the dividend yield remains relatively stable, around 2.4% to 2.6%, indicating consistent returns to shareholders through dividends. Additionally, sales per share show a steady increase from 15.7 in December 2022 to 19.0 in December 2026, reflecting positive sales growth and potentially increased market share.
Overall, the forecasted financial metrics for LVMH suggest a company with stable valuation and profitability over the next few years. Key ratios such as P/E, EV/EBITDA, and EV/EBIT show initial fluctuations but trend towards stabilization, indicating potential market confidence in LVMH’s long-term performance. The consistent growth in book value and sales per share highlights positive business performance, while the stable dividend yield and return metrics provide steady returns for investors.
7. Risks and Mitigation
7.1 Risks
7.1.1 A Slowing Global Economy
LVMH faces several significant economic risks that could impact its operations and financial performance. One of the primary risks is global economic downturns, which can lead to reduced consumer spending on luxury goods and decreased tourist purchases, significantly affecting sales and revenue. Economic recessions may also force LVMH to cut back on marketing and expansion investments. Fluctuations in currency exchange rates pose another critical risk, leading to revenue volatility and increased production costs, which complicate pricing strategies across different markets. Additionally, rising inflation and interest rate increases can squeeze profit margins by raising costs for raw materials, production, and transportation, while also reducing consumers' disposable income and spending power. Economic disparities between regions can lead to uneven market performance and complicate investment allocation decisions. Moreover, commodity price volatility can affect the cost of high-quality materials used in luxury goods, potentially eroding profit margins if increased costs cannot be passed on to consumers. By identifying and managing these economic risks proactively, LVMH can enhance its resilience and maintain its market position despite economic challenges.
7.1.2 Dependence On Key Markets
LVMH's dependence on key markets, particularly China and the United States, presents significant risks to its operations and financial stability. Economic or political changes in these critical regions can dramatically impact the company's sales and profitability. For example, an economic slowdown in China or increased trade tensions between the U.S. and other countries could lead to reduced consumer spending on luxury goods. Additionally, regulatory changes or political instability in these markets can disrupt business operations and supply chains. This heavy reliance on a few major markets makes LVMH vulnerable to localized downturns or geopolitical issues, potentially leading to substantial revenue fluctuations and operational challenges.
7.1.3 Brand And Reputation Risks
LVMH faces significant brand and reputation risks, which are crucial given the company's status as a leader in the luxury goods market. Negative publicity, such as scandals or quality issues, can severely damage consumer trust and diminish the brand's perceived value. For instance, any involvement in unethical practices, such as labor violations or environmental damage, can attract widespread criticism and lead to consumer boycotts. Furthermore, the luxury sector is particularly vulnerable to counterfeiting and intellectual property theft, which can erode brand equity and reduce sales by flooding the market with inferior, fake products that tarnish the brand's image.
In addition to these risks, the growing consumer focus on sustainability and corporate social responsibility presents a challenge for LVMH. Today's consumers, particularly younger generations, are increasingly demanding that brands operate ethically and sustainably. Failure to meet these evolving expectations can result in significant reputational damage and a loss of market share to competitors who better align with consumer values. For example, if LVMH's sustainability efforts are perceived as insufficient or inauthentic, it could lead to negative media coverage and a decline in consumer loyalty.
7.2 Mitigation
7.2.1 A Multifaced Strategy For A Strong Company
To mitigate these economic risks, LVMH can adopt a multifaceted strategy. Diversifying its product lines to include more affordable luxury options and expanding into emerging markets with growing middle classes can help cushion against declines in established markets. Utilizing financial hedging instruments and balancing costs and revenues in the same currencies can manage currency fluctuation risks. Implementing cost control measures and seeking supply chain efficiencies can address rising inflation and interest rate impacts, while flexible pricing strategies can help pass some increased costs to consumers without significantly affecting demand. Developing tailored regional strategies and maintaining a flexible investment approach allows LVMH to quickly adjust to varying economic conditions across different markets. Finally, securing long-term contracts with suppliers, diversifying sourcing, and innovating in product design and manufacturing processes to use materials more efficiently can mitigate the risks associated with commodity price volatility. By proactively implementing these measures, LVMH can strengthen its resilience against economic uncertainties.
7.2.2 Geographical Diversification Is Key
To mitigate the risks associated with dependence on key markets, LVMH can adopt several strategies. Diversifying its geographical presence by expanding into emerging markets with growing middle classes, such as India, Southeast Asia, and Latin America, can reduce reliance on any single market. This strategy helps balance the impact of economic or political changes in major markets like China and the United States. Additionally, developing tailored products and marketing strategies that cater to local tastes and preferences can enhance market penetration and consumer loyalty in these new regions.
LVMH can also invest in strengthening its digital and e-commerce capabilities to reach a broader global audience, making it less dependent on physical retail performance in any particular market. Enhancing supply chain flexibility and resilience by diversifying suppliers and manufacturing locations can further mitigate risks related to geopolitical issues and regulatory changes. By implementing these measures, LVMH can create a more balanced and robust global presence, reducing its vulnerability to market-specific downturns and ensuring more stable revenue streams.
7.2.3 Meeting The Changing Consummer Demand
To mitigate the various brand and reputation risks facing LVMH, the conglomerate employs a comprehensive set of strategies. Firstly, LVMH maintains stringent quality control measures across all its products and services, ensuring that each item upholds the highest standards of craftsmanship and excellence. This commitment to quality helps safeguard the brand's reputation for luxury and exclusivity. Additionally, LVMH actively combats counterfeiting through robust anti-counterfeiting measures, protecting both its brand integrity and consumers from counterfeit goods. The conglomerate carefully manages brand extensions and collaborations to prevent brand dilution, ensuring that each new venture aligns with the luxury image and values of its core brands. Moreover, LVMH has established crisis management protocols to swiftly and effectively respond to any incidents that may arise, safeguarding its reputation in times of adversity. By staying attuned to shifting consumer perceptions and market trends, prioritizing corporate social responsibility initiatives, and maintaining compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, LVMH continues to mitigate brand and reputation risks, reinforcing its position as a leader in the luxury goods industry.
8. ESG Assessment
While LVMH's product portfolio primarily focuses on luxury goods, the company is actively engaging in environmentally and socially responsible activities to contribute to sustainable development goals. LVMH is committed to sustainability through initiatives such as reducing carbon emissions, promoting circular economy practices, and supporting biodiversity. The company aims to enhance its environmental performance by increasing the use of renewable energy, minimizing waste, and improving the sustainability of its supply chain.
8.1 Environmental Assessment
In 2023, LVMH made significant strides in its commitment to sustainability by enhancing its renewable energy usage and reducing its carbon footprint. The proportion of renewable energy in LVMH's energy mix surged to 63%, a notable increase from 47% in 2022. This achievement was driven by a proactive approach that maximized the use of biogas and a concerted campaign by LVMH’s Maisons to establish framework agreements with renewable energy suppliers.
Additionally, the implementation of an energy efficiency plan, announced in September 2022, contributed to substantial reductions in energy-related CO2 emissions. Between 2019 and 2023, LVMH achieved a reduction of over 28% in CO2 emissions across Scopes 1 and 2. This progress was also supported by bold initiatives aimed at minimizing the environmental footprint of LVMH stores. For instance, in December 2023, LVMH launched partnerships with leading shopping mall developers, including Hang Lung Properties, and key lessors in the United Arab Emirates, signed at the COP28 summit, as well as with the Miami Design District. These collaborations focus on improving the environmental impact of mall stores, further advancing LVMH's sustainability objectives.
To address Scope 3 emissions, which constitute 95% of the Group’s carbon footprint, LVMH expanded its environmental strategy with the introduction of the LIFE 360 Business Partners program. This new initiative is designed to support and guide suppliers in achieving significant reductions in their carbon emissions, water usage, and biodiversity impact. The program aims to provide suppliers with access to LVMH's training programs, regulatory updates, and expert solutions, enabling them to make meaningful progress in reducing their environmental footprint.
The LIFE 360 Business Partners program builds on the supplier transition plans already implemented by several of LVMH’s Maisons. By offering comprehensive support to suppliers, LVMH is not only enhancing its own sustainability practices but also driving systemic change within its supply chain. This initiative is crucial for LVMH to meet its ambitious target of cutting Scope 3 emissions by 55% per unit of added value by 2030, a goal validated by the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi).
Through these concerted efforts, LVMH demonstrates its dedication to sustainability and its proactive role in mitigating environmental impact. By leveraging renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, and fostering collaboration with partners and suppliers, LVMH is paving the way for a more sustainable future while maintaining its leadership in the luxury goods industry.
8.1 Social Assessment
LVMH's Diversity & Inclusion Policy is spearheaded by the Executive Committee at the global level and includes specific quantitative targets. Key initiatives focus on increasing opportunities for all talented individuals. One significant target is to increase the proportion of leadership roles occupied by women. With women making up 71% of LVMH's workforce, the EllesVMH program aims to ensure that half of all strategic roles are held by women by 2025. As of 2023, women occupied 46% of these key roles. The program also advocates for equal pay and skills development through the EllesVMH networks, offering training and career development tools via the EllesVMH.com platform.
LVMH is also dedicated to recruiting and developing individuals with disabilities. For around fifteen years, LVMH has focused on integrating people with disabilities into its workforce and is a member of the International Labour Organization’s Global Business and Disability Network. The goal is for people with disabilities to comprise 2% of the global workforce by 2025. This initiative is managed by LVMH’s Disability Inclusion Office, which supports the recruitment and professional growth of employees with disabilities. Specific programs include Sephora’s U.S. logistics centers, where 10% of employees have disabilities, and a partnership in France to include autistic individuals. Additionally, LVMH has been enhancing the digital accessibility of its websites since 2022.
Lastly, In 2023, LVMH invested over €189 million, amounting to 1.8% of its gross payroll, to enhance employee working conditions. This included €44.2 million dedicated to health and safety initiatives such as purchasing protective equipment, hiring occupational health officers, and providing training programs. The Group's Maisons implemented these commitments through tailored initiatives specific to their teams' needs. For instance, Hennessy introduced two safety-related training programs: Leadership Sécurité for managers and Cap Prévention for non-managerial staff. Additionally, Hennessy focused on machinery safety compliance by auditing production lines, addressing non-compliance issues, and providing necessary training.
8.3 Governance Assessment
LVMH's sustainability initiatives under the governance pillar emphasize robust corporate governance, ethical conduct, and comprehensive risk management. The Group's governance approach integrates strict adherence to ethical standards, transparency in operations, and active stakeholder engagement, aiming to ensure sustainable and responsible business practices.
At the core of LVMH's governance framework is the Sustainability Committee, which oversees the Group’s environmental, social, and governance (ESG) strategy. This committee plays a crucial role in embedding sustainability principles across all aspects of LVMH’s operations and decision-making processes. The Group has implemented a comprehensive Code of Conduct that outlines the ethical guidelines and business practices expected of all employees and stakeholders. This Code emphasizes integrity, accountability, and the importance of maintaining high ethical standards in all business dealings.
Similarly, LVMH is increasingly integrating environmental and social goals into employee compensation, including senior executives and managers. For instance, in January 2023, the Board of Directors considered these targets when determining annual variable compensation for key executives. Qualitative targets affect 40% of compensation, with 25% of criteria tied to the Group's ESG performance, including initiatives like LIFE 360 and promoting ethical awareness among employees.
To support these ethical standards, LVMH has established rigorous compliance measures, including detailed anti-corruption policies and extensive training programs for employees. These programs are designed to foster a culture of ethical behavior and ensure compliance with global standards. Regular audits and assessments are conducted to monitor compliance, identify areas for improvement, and reinforce the Group's commitment to ethical conduct.
9. Conclusion
In a nutshell, LVMH represents a compelling investment opportunity due to its unparalleled portfolio of iconic brands, strong financial performance, and strategic market positioning. The company's diversified business model, spanning fashion, leather goods, perfumes, cosmetics, watches, jewelry, wines, and spirits, ensures resilience and stability even in fluctuating economic conditions. With a total revenue of €79.2 million in 2023 and significant contributions from all its segments, LVMH showcases robust growth and profitability.
Moreover, LVMH's commitment to innovation, sustainability, and excellence in craftsmanship keeps it at the forefront of the luxury industry. Its global presence and strong brand equity drive consumer demand and market expansion, particularly in emerging markets like Asia. The company's solid financial health, with substantial assets, equity, and manageable debt levels, provides a strong foundation for future investments and acquisitions, further enhancing its market leadership.
Additionally, LVMH's strategic acquisitions, such as Tiffany & Co., bolster its portfolio and open new growth avenues in high-end markets. The company's dedication to rewarding shareholders through consistent dividend growth reflects its strong cash flow and profit generation capabilities. Given these factors, LVMH is well-positioned for sustained long-term growth, making it an attractive investment for those seeking exposure to the thriving luxury goods sector.
*Do note that all of this is for information only and should not be taken as investment advice. If you should choose to invest in any of the stocks, you do so at your own risk.
10. References
Altagamma, & Bain & Company. (2022). Worldwide luxury market monitor 2022. Luxe Digital. Retrieved from: https://cdn.luxe.digital/download/Altagamma-Bain-Worldwide-Luxury-Market-Monitor-2022-luxe-digital.pdf
Bain & Company. (2023, January 19). Global luxury market projected to reach $1.5 trillion in 2023, a new record for the sector as consumers seek luxury experiences. [Press release]. Retrieved from: https://www.bain.com/about/media-center/press-releases/2023/global-luxury-market-projected-to-reach-1.5-trillion-in-2023-a-new-record-for-the-sector-as-consumers-seek-luxury-experiences/
Deloitte Global. (2023). Global Powers of Luxury Goods 2023. Retrieved from: https://www.deloitte.com/global/en/Industries/consumer/analysis/gx-cb-global-powers-of-luxury-goods.html
Statista (n.d.). Global luxury goods market size from 2023 to 2030. Retrieved from: https://www.statista.com/outlook/cmo/luxury-goods/worldwide
Fortune Business Insights (n.d.). Luxury goods market size, share & industry analysis, regional outlook, application development, growth potential, key players and forecast 2023 - 2030. Retrieved from: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/luxury-goods-market-103866
LVMH. (2023). LVMH committed to positive impact 2023. Retrieved from: https://r.lvmh-static.com/uploads/2024/04/lvmh_committed_to_positive_impact_2023-1.pdf
LVMH. (2024, January 31). LVMH - Financial documents - LVMH December 31, 2023. Retrieved from: https://r.lvmh-static.com/uploads/2024/01/financial-documents-lvmh-december-31-2023.pdf
Quartr. (n.d.). The luxury empire: LVMH’s most notable acquisitions since inception. Retrieved from: https://quartr.com/insights/company-research/the-luxury-empire-lvmh-s-most-notable-acquisitions-since-inception







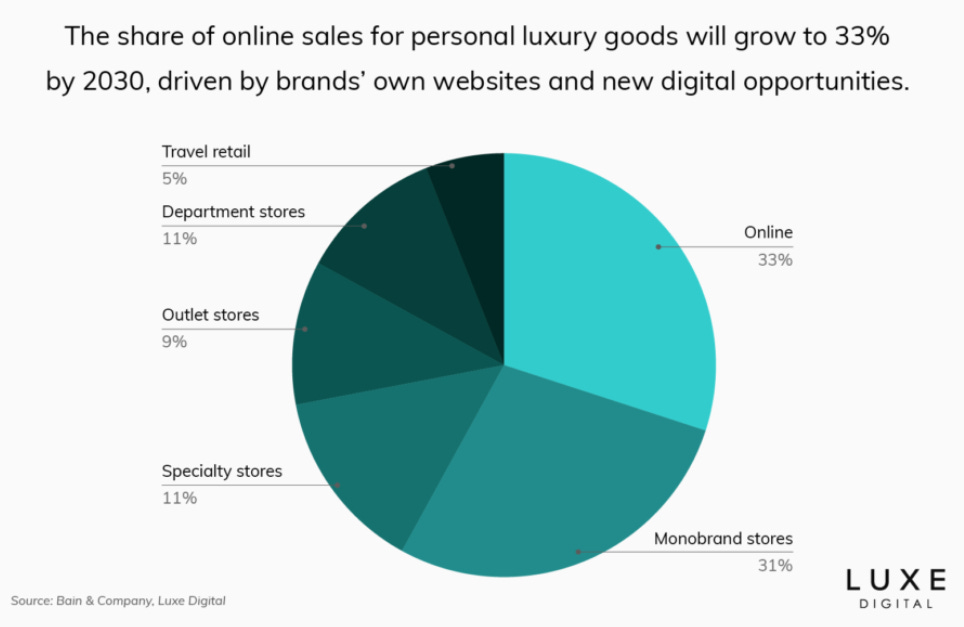




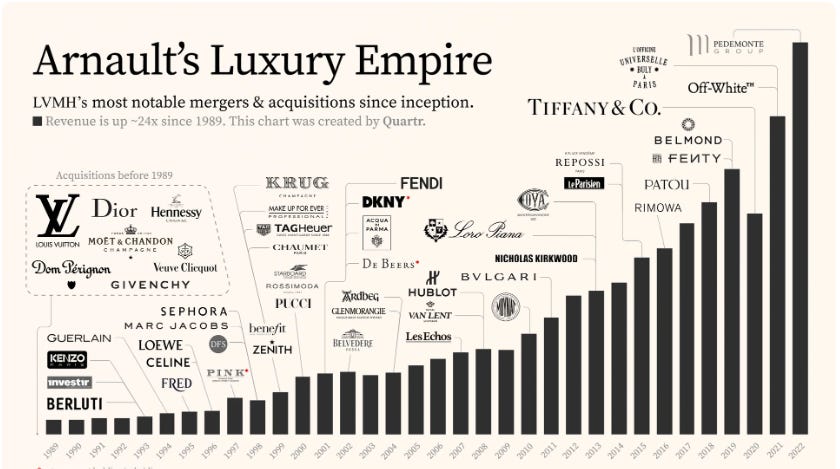









Have a few questions about this write-up:
1) LVMH is structured such that it grew as a conglomerate. it was traditional french luxury powerhouses that it rebranded which caused it to be so big (LV, dior etc). It is especially notable because it failed to capture Gucci and Hermes, traditional french luxury. When it comes to consumer preferences, and when people look at French brands, the question is therefore how it can compete against Hermes and Gucci and their respective brands. So how will it? Hermes is increasingly emerging as a faster grower than LVMH which is sluggish with its many brands and slower growth rates.
2) You talk about the chinese consumer market hitting 45% of luxury market. what's your thoughts on the chinese conusmer downgrade? is this not very detrimental to the world of luxury, especially given talks of tariffs and prices being even higher, would chinese conusmers choose to downgrade and move to the second hand goods market more preferentially?
3) When you referred to sustainability and the circular economy, you gave very specific company examples. however, this forgets that LVMH is bigger than one brand and its value proposition (and also weakness) is that it owns many brands. Because of that, it has to be a group wide strategy for it to affect any change. each brand has its own CEO and their own team. therefore, do you have any group wide dynamics that follows these trends instead?
4) when we think of LVMH, we think of acquisitions. i think this is a larger driver than anything else it might have because growth for such a big company will be slower, and investors associate LVMH with bernard arnold's acquisition strategies. do you see any in the pipeline?